Reusable industrial packaging systems are becoming an essential component in modern supply chains. As industries seek to reduce waste, lower costs, and improve sustainability, the shift from single-use packaging to reusable alternatives is gaining momentum.
These systems offer a practical, efficient way to transport, store, and protect goods across multiple cycles, providing significant environmental and economic benefits.
The rise of reusable packaging in industry
Industrial sectors have traditionally relied on disposable packaging materials such as cardboard boxes, plastic wraps, and wooden pallets. While convenient, these single-use options contribute heavily to landfill waste and often lack durability for repeated use.
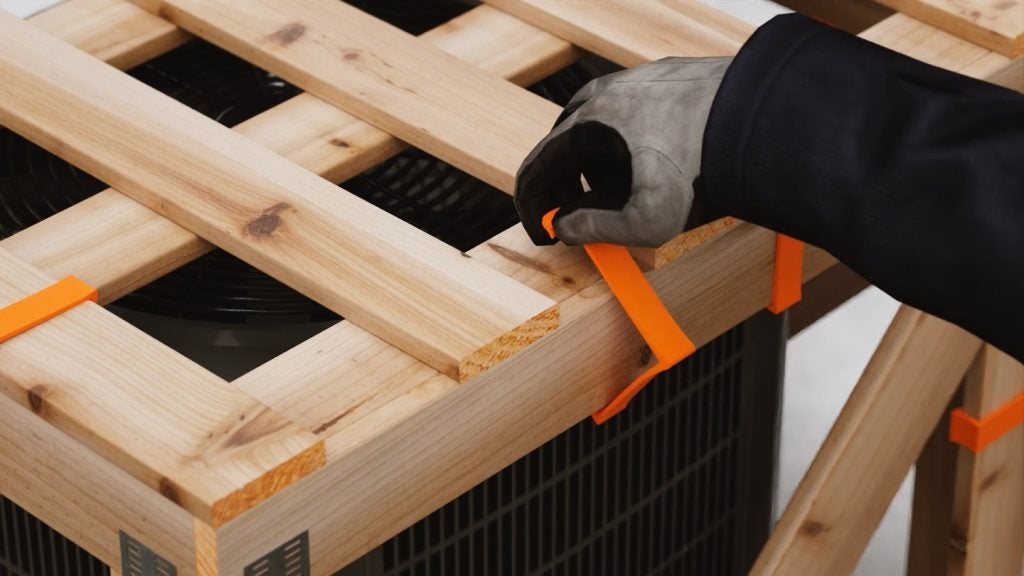
Reusable industrial packaging systems, including heavy-duty containers, pallets, crates, and bulk bins, are engineered to withstand multiple shipments, reducing the need for constant replacement.
The push for greener operations and regulatory pressures on waste management have accelerated the adoption of reusable packaging. Companies now view these systems not only as a means to decrease environmental impact but also as a strategic investment in supply chain resilience.
By reusing packaging materials, firms reduce raw material consumption and waste disposal costs, while improving handling efficiency and product safety.
Technological advancements have also played a role in the rise of reusable packaging. Innovations in materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene offer strong, lightweight solutions that resist damage during transit.
Some systems incorporate RFID tracking and barcoding, enabling better inventory management and traceability throughout the packaging lifecycle.
Key benefits of reusable industrial packaging systems
One of the primary advantages of reusable industrial packaging is its positive effect on sustainability. By using packaging that can be cleaned, repaired, and reused, companies drastically cut down on waste generation.
This supports corporate social responsibility initiatives and aligns with global sustainability goals, including those related to the circular economy.
From an economic perspective, reusable packaging lowers long-term operational costs. Although the initial investment may be higher than disposable alternatives, the ability to cycle packaging multiple times yields cost savings over the product lifecycle.
It also minimises supply chain disruptions by reducing packaging shortages and the frequency of purchasing new materials.
Durability is another important benefit. Reusable industrial containers are designed to protect goods from damage during handling and transport, which reduces product loss and associated costs. They can be customised to fit specific product dimensions, improving space utilisation and reducing freight expenses.
Moreover, reusable systems often feature ergonomic designs, making them easier and safer to handle for workers.
This reduces workplace injuries and increases productivity. Some packaging solutions are stackable and collapsible, optimising storage space when not in use and further contributing to operational efficiency.
Challenges and considerations in implementing reusable systems
Despite the clear advantages, switching to reusable industrial packaging requires careful planning and management. One key challenge is establishing an effective reverse logistics process to collect, inspect, and return packaging for reuse.
Without a streamlined system, the benefits can be undermined by logistical inefficiencies.
Maintenance and cleaning protocols are essential to ensure reusable packaging remains safe and functional. This is particularly critical in industries with stringent hygiene standards, such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Companies must invest in appropriate cleaning facilities or outsource these services to specialised providers.
Another consideration is the upfront cost and complexity of adopting reusable systems. Businesses need to evaluate the total cost of ownership, factoring in purchase price, maintenance, transportation, and the expected number of reuse cycles. Tailoring packaging solutions to specific supply chains can require custom design work and coordination with suppliers and logistics partners.
In addition, compatibility with existing equipment and storage facilities must be reviewed to avoid operational disruptions. Training staff on new handling procedures and system use is necessary to maximise the benefits and prevent damage or misuse.
Looking ahead: the future of reusable packaging in industry
The future of reusable industrial packaging looks promising, with innovation and sustainability driving continuous improvement. As circular economy principles become central to corporate strategy, reusable systems will be integral to reducing the environmental footprint of supply chains.
Emerging technologies such as smart packaging with embedded sensors and IoT connectivity promise to enhance monitoring and management of reusable packaging assets. This will improve tracking, condition monitoring, and data analytics, enabling more efficient reuse cycles and reducing losses.
Materials science continues to advance, delivering more sustainable and durable materials that extend the life of reusable packaging while lowering its environmental impact.
Biodegradable and recyclable composites are also being explored for hybrid solutions combining reusability with eco-friendly disposal options.
Industry collaboration will be crucial in scaling reusable packaging adoption. Sharing best practices, developing common standards, and building shared logistics networks can reduce costs and improve system effectiveness.
In summary, reusable industrial packaging systems represent a forward-thinking approach to packaging challenges faced by today’s industries.
They offer a sustainable, cost-effective, and practical solution for modern supply chains, poised to play a vital role in building a more circular and resilient future.