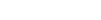
Injectable drug packaging is a critical component of modern healthcare, ensuring that medications remain safe, stable, and effective from production to patient use.
Innovations in this field are transforming how drugs are delivered, improving patient safety, convenience, and treatment outcomes.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
From vials and ampoules to prefilled syringes and wearable injectors, packaging design has become a key factor in the effectiveness of injectable therapies.
Evolving materials for safer packaging
Traditionally, glass has been the standard material for injectable drug packaging due to its inert properties and ability to maintain drug stability. Yet, modern challenges like delamination—where tiny glass flakes can contaminate the medication—have driven the development of alternative materials.
Cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) and cyclic olefin polymer (COP) are now widely used, offering durability, chemical resistance, and minimal risk of contamination.
Plastic materials such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) have also gained popularity.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataTheir lightweight, shatter-resistant nature makes them particularly suitable for a wide range of injectable formulations, helping to reduce breakage risks during transportation and handling.
Design innovations for convenience and safety
Packaging design has advanced significantly to improve both patient experience and safety. Prefilled syringes, autoinjectors, and wearable injector devices are leading this evolution.
These innovations allow patients to self-administer medications safely and accurately, particularly for chronic conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
These devices not only enhance dosing accuracy but also reduce the risk of needle-stick injuries. In parallel, improvements in aseptic processing and sterilisation techniques ensure that injectable medications remain free from microbial contamination, maintaining their efficacy throughout the product’s shelf life.
Market trends and future prospects
The global injectable drug packaging market is experiencing rapid growth.
Driven by the rise of biologic therapies, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and demand for ready-to-use (RTU) solutions, the market is projected to expand significantly over the coming years.
Prefilled and pre-assembled delivery systems are particularly in demand, as they minimise preparation time and reduce errors during administration.
The continued focus on safety, convenience, and regulatory compliance is shaping the future of injectable drug packaging.
Innovations in materials, design, and delivery mechanisms ensure that patients worldwide receive therapies that are not only effective but also easy and safe to use.